Mélangeur émulsifiant : introduction, principe de fonctionnement, types et produits d'application

Top 10 des fabricants mondiaux de machines d'enrobage de comprimés en 2024
Le guide ultime de la machine homogénéisatrice
Introduction
Le machine homogénéisatrice est un appareil utilisé pour homogénéiser des substances en les cassant et en les mélangeant. C'est un outil de base dans de nombreuses entreprises, en particulier lorsque les produits alimentaires et pharmaceutiques exigent des textures homogènes. Dans ce guide, nous allons essayer de couvrir ce qu'est une machine d'homogénéisation, comment elle fonctionne et pourquoi elle est essentielle dans de nombreuses industries, en particulier l'industrie alimentaire. Nous discuterons également des différences entre un homogénéisateur et un émulsifiant, car ces termes sont parfois utilisés de manière incorrecte.
Qu'est-ce qu'une machine homogénéisatrice ?
À haute pression, l'homogénéisateur mélange et applique une haute pression à un groupe d'ingrédients, ce qui provoque la décomposition des plus grosses particules en particules plus petites et de taille homogène. La consistance commune du mélange sans signes de regroupement ni de texture inégale est maintenue pendant ce processus. Les homogénéisateurs peuvent être utilisés dans les industries de transformation des aliments, des médicaments, des cosmétiques et de la biotechnologie.
Un exemple est la machine d'homogénéisation, qui est utilisée pour le lait transformé dans l'industrie alimentaire. Chaque fois que les molécules de graisse du lait sont émulsionnées par la machine et ne se déposent pas au fond, elle produit un lait standard, homogène et épais.
Quelle est la différence entre un homogénéisateur et un émulsifiant ?
Bien que les homogénéisateurs et les émulsifiants mélangent les liquides et les solides pour obtenir une forme homogène, leurs objectifs sont plutôt différents. Un émulsifiant se concentre sur la stabilisation de deux ingrédients qui sont insolubles l'un dans l'autre, comme l'huile et l'eau ; un homogénéisateur fonctionne principalement sous pression. Parmi les agents les plus courants, on trouve des agents qui créent une liaison entre les deux ingrédients afin de produire le mélange appelé émulsions.
En termes plus simples :
- Les homogénéisateurs réduisent la taille et l’uniformité des particules liquides.
- Les émulsifiants, qui nécessitent souvent un agent chimique, facilitent le mélange de deux ou plusieurs phases, à savoir l'eau et l'huile.
Par exemple, l'émulsification peut être utilisée pour combiner des ingrédients liposolubles et des ingrédients en phase aqueuse dans la mayonnaise, tandis que l'homogénéisation peut être utilisée pour réduire la taille des particules des ingrédients à une taille de particule plus fine pour une texture plus lisse.
Comment fonctionne le processus d’homogénéisation ?
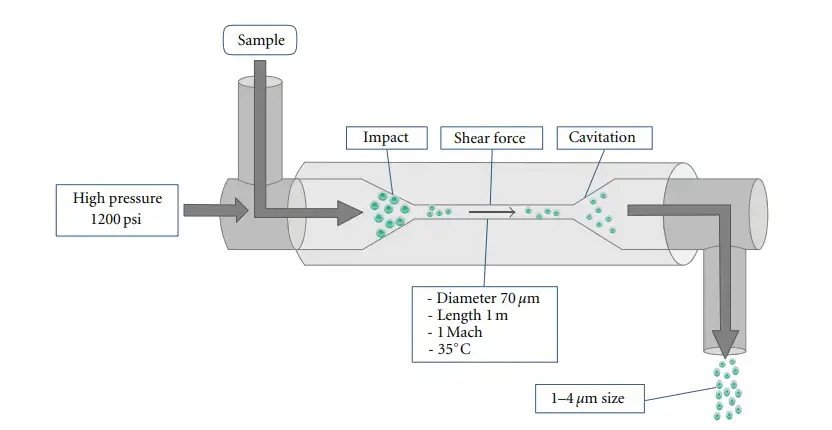
principe de fonctionnement
Une forte pression est appliquée au processus d'homogénéisation. Grâce à cette pression, ce mélange est forcé à travers de petits tubes ou vannes. Ces tubes ou vannes séparent les plus grosses particules en très petites particules, et c'est ainsi qu'ils fonctionnent. Ces étapes simples peuvent être utilisées pour décomposer le processus :
- Préparation: Certains des mélanges nécessitant une homogénéisation sont ajoutés à la machine lorsqu’ils sont prêts à être utilisés.
- Haute pression : La pression varie de 0,5 à 15 000 psi, ce qui correspond à la force en livres par pouce carré, selon les exigences du travail.
- Décomposition des particules :Grâce à l’utilisation d’un broyeur à granulés, il est plus facile de former de petites particules à partir de grosses particules et d’affiner une taille uniforme.
- Distribution uniforme :Toutes les particules sont uniformément réparties les unes par rapport aux autres, une caractéristique qui donne une texture lisse au mélange.
De nombreuses industries alimentaires, comme celles qui manipulent des produits laitiers, éliminent le lactose en utilisant cette méthode pour rendre le lait, le yaourt et le fromage soyeux.
Quelle est l’utilité des homogénéisateurs dans l’industrie alimentaire ?
Dans l'industrie alimentaire, l'homogénéisateur est largement utilisé pour garantir que tous les aliments ont la même texture et durent plus longtemps. Voici comment il est le plus souvent utilisé :
- Produits laitiers : Les mélangeurs sont indispensables pour préparer le lait, la crème et le yaourt. Mais en plus d'empêcher la formation d'une couche et de donner au lait une texture lisse, il émulsionne les particules de graisse qu'il contient.
- Sauces et vinaigrettes : Un procédé d'émulsification est utilisé pour conserver les ingrédients à base d'huile et d'eau dans les pâtes à tartiner ainsi que dans les vinaigrettes et articles similaires tout en leur conférant une finition uniforme.
- Jus et boissons : L'homogénéisation par pulpage permet aux pulpes ou aux fibres des jus d'avoir le même degré de granulométrie.
- Glace: L'homogénéisation garantit que les matières grasses de la crème et du lait sont réparties uniformément, ce qui donne à la crème glacée une texture plus lisse que les gens apprécient.
Une étude publiée en 2017 dans le Journal of Dairy Science a révélé que l’homogénéisation rend le lait beaucoup plus stable, ce qui signifie que la graisse est moins susceptible de se séparer au fil du temps.
Quelle est la fonction d'un homogénéisateur ?
Un homogénéisateur est principalement utilisé pour rendre un mélange plus homogène et, en général, il a pour fonction spécifique de décomposer les grosses particules du mélange en particules plus petites. Il s'agit d'un processus qui affine la surface d'un produit et empêche les ingrédients de se séparer, ce qui améliore la stabilité et la sensation.
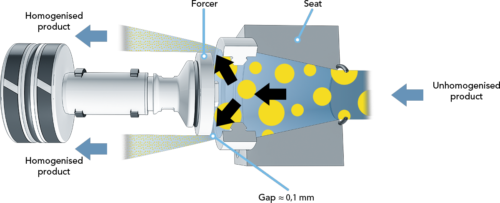
fonction homogénéisateur
Dans les applications pharmaceutiques, par exemple, un homogénéisateur garantit une répartition équitable des composants du médicament, facilitant ainsi la distribution appropriée du médicament lors de la prise. Les médicaments liquides dépendent particulièrement de cette capacité, car le bon dosage dépend de la consistance.
Quel est le but de l’homogénéisation ?
La standardisation est utile pour garantir qu'une bonne chose ne change pas d'un moment à l'autre et d'un endroit à un autre. Dans les produits alimentaires, elle empêche la détérioration de la qualité et facilite la durée de conservation en empêchant la séparation des ingrédients. De plus, en améliorant la sensation au toucher des produits, l'homogénéisation les rend plus lisses et plus attrayants pour les acheteurs.
Par exemple, dans le domaine cosmétique, lors de la fabrication de lotions, de crèmes et d'autres produits de soin de la peau à la texture lisse qui ne se sépare pas au fil du temps, l'homogénéisation est essentielle. Elle est utilisée en biotechnologie pour disséquer les structures cellulaires dans le cadre de tels processus de recherche et développement.
Conclusion
Les homogénéisateurs sont très populaires dans diverses industries, de la fabrication alimentaire aux laboratoires. Ils contribuent à garantir que les produits sont stables, homogènes et lisses, améliorant ainsi la durée de conservation. Les homogénéisateurs sont parfois confondus avec les émulsifiants, étant donné que les homogénéisateurs soumettent principalement les mélanges à une séparation, contrairement aux émulsifiants, qui favorisent principalement l'adhésion d'éléments qui seraient autrement incapables de se mélanger.
De la production de produits laitiers jusqu'à la création de sauces et même de produits de soin pour la peau, c'est l'homogénéisateur qui permet aux fabricants d'obtenir une régularité dans la production des meilleurs produits qui répondront aux besoins des consommateurs. Aujourd'hui, l'industrie moderne doit absolument compter sur l'homogénéisation pour garantir l'intégrité des mélanges lorsqu'ils sont sur les étagères ou entre les mains du consommateur.
Questions fréquemment posées (FAQ)
Quel est le but principal d’un homogénéisateur ?
Le but d'un homogénéisateur est de réduire les particules les plus grosses à des tailles plus petites afin que le texte et la composition d'un mélange soient cohérents. Il stabilise le produit et réduit également la séparation.
En quoi l’homogénéisation diffère-t-elle de l’émulsification ?
Pour l'émulsification, deux liquides, comme l'huile et l'eau, et parfois un agent émulsifiant, sont incorporés, et pour l'homogénéisation, ou la décomposition des particules, une pression est appliquée.
Pourquoi l’homogénéisation est-elle importante dans l’industrie alimentaire ?
Dans le secteur alimentaire, l'homogénéisation est essentielle pour garantir une stabilité constante et une texture lisse des produits. Elle garantit que le lait, les sauces et les crèmes restent homogènes au fil du temps, évite la séparation des ingrédients et prolonge la durée de conservation.




