Customer Visit Grand: Austrian Client Explores Capsule Filling Technology

Vegetable Capsules: Benefits, and Capsule Filling Machine Compatibility
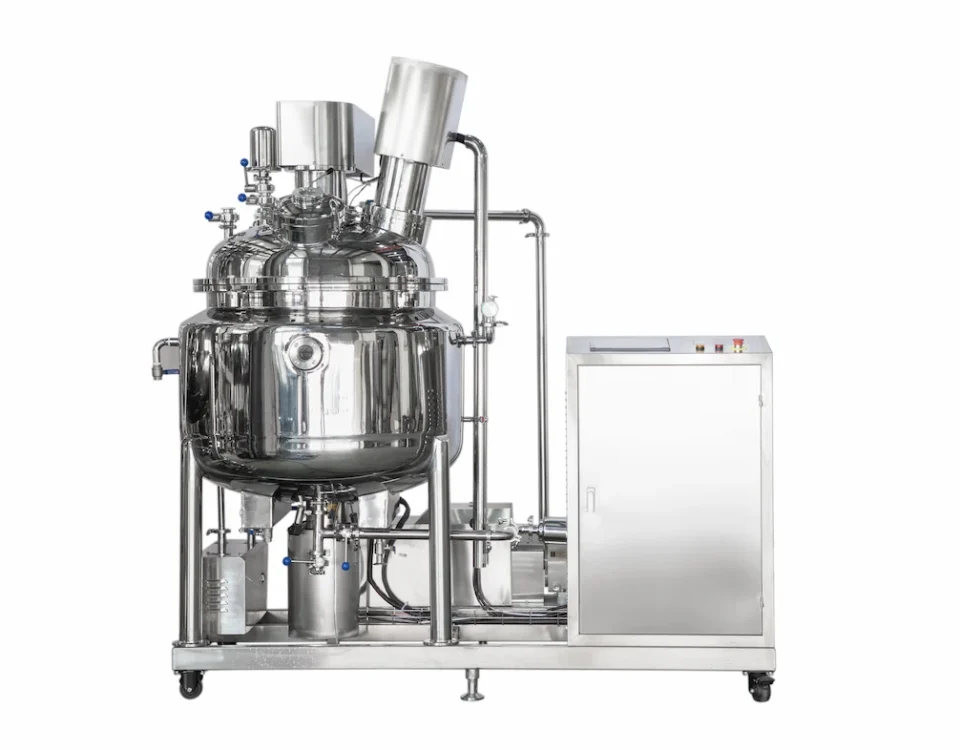
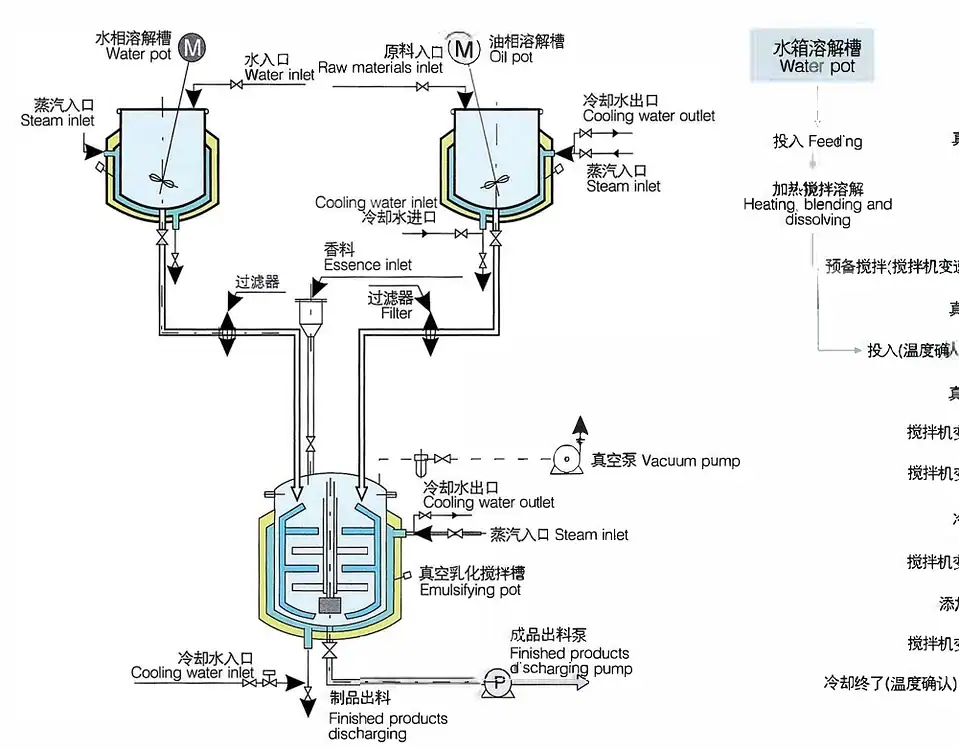
Vacuum Emulsifying Tank Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Introduction
Pharmaceutical manufacturers know that achieving a stable, homogenous cream or ointment is critical for product efficacy and shelf life.
Recent research highlights how mixing under vacuum can dramatically improve emulsion stability. For example, studies note that air bubbles introduced during traditional mixing can destabilize emulsions, leading to issues like creaming and phase separation.
A vacuum emulsifying tank avoids this by mixing under reduced pressure to eliminate entrapped air, resulting in smoother, more uniform emulsions. This high-shear emulsification in pharma processes also produces finer droplet sizes, which further enhances emulsion stability and consistency. In this article, we’ll explore why vacuum emulsifying tanks are revolutionizing pharmaceutical cream production, backed by academic and industry research, and how their technical features translate into real benefits for buyers in the pharmaceutical industry.

Why Use Vacuum Emulsifying Tanks for Pharmaceutical Creams?

A comparison of gel produced without vacuum (left, cloudy due to air bubbles) versus with vacuum (right, clear and bubble-free). Vacuum mixing yields a more transparent, stable product by eliminating entrapped air.
In cream and ointment manufacturing, product quality is paramount. A vacuum emulsifying tank offers distinct advantages in product consistency and stability. By mixing ingredients under vacuum, it removes air bubbles that would otherwise be trapped in the cream, preventing those bubbles from causing oxidation or instability in the formulation. The result is a more stable emulsion with enhanced homogeneity – no unsightly air pockets or “foamy” texture. Visually, vacuum-mixed creams tend to be smoother and glossier, with no visible bubbles, giving a more professional appearance. Functionally, eliminating air improves the cream’s performance: the product won’t separate or lose potency over time due to trapped oxygen. Research in pharmaceutical mixing confirms that vacuum mixing produces creams with finer dispersion of active ingredients, which can lead to better drug release and absorption in the body. In short, a vacuum emulsifying tank ensures that pharmaceutical creams and gels come out with consistent texture, stability, and efficacy, batch after batch.
High Shear Emulsification in Pharma: Fine Particles and Uniform Blends
Pharmaceutical creams often contain oils, water-based components, and active ingredients that need to be emulsified into a uniform mixture. Vacuum emulsifying tanks integrate high-shear homogenizers (rotor-stator mixers) to break down droplets and particles to microscopic sizes. This is crucial because droplet size directly impacts emulsion stability – smaller droplets yield more stable emulsions.
The high-shear emulsifier in a vacuum tank can spin at speeds up to ~3,600 rpm, creating intense turbulence and shear forces. Under these conditions, immiscible phases (like oil and water) are rapidly dispersed into each other, producing an exceptionally fine emulsion. Importantly, doing this under vacuum means there’s no air to interfere with the mixing process; all the mixer’s energy goes into emulsification rather than creating foam.
Academic and industry reports note that vacuum high-shear mixing can achieve particle sizes on the order of just a few microns or even sub-micron range, which is beneficial for pharmaceutical creams that require a smooth feel or enhanced delivery of active compounds. This level of pharmaceutical-grade emulsifying tank performance ensures each dose of cream has uniform composition, critical for meeting stringent pharma quality standards.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Cream Production and More
Vacuum emulsifying tanks have become the go-to solution for pharmaceutical cream production, as well as a range of other semi-solid and liquid products. They are commonly used for making dermatological creams, medicinal ointments, gels (e.g. ultrasound gels or hand sanitizers), and even suspensions and syrups that require uniform consistency. For example, in producing a medicated cream for skin conditions, a vacuum emulsifier will homogenize the active drug with the cream base and remove air to prevent any voids in the final product.

Ointments that are thick and hard to mix (high viscosity) particularly benefit from the vacuum tank’s ability to mix without entraining air, yielding a smooth, easily applicable product. Even specialized formulations like nano-emulsions or gel-based vaccines can be prepared with such equipment, since the high shear under vacuum can achieve the necessary particle size and sterility.
Industry trends underscore the importance of this technology: with the growing demand for advanced topical and transdermal therapies, many pharma companies are investing in modern vacuum emulsifying mixers to stay competitive. In fact, market research projects the pharmaceutical mixing equipment market to reach $1.7 billion by 2025, with vacuum emulsification systems accounting for a significant share as manufacturers prioritize quality and consistency. Whether it’s a vacuum emulsifying tank for pharmaceutical cream production or for R&D of new gel formulations, this equipment has become indispensable in pharma manufacturing facilities worldwide.
Key Features of a Pharmaceutical-Grade Emulsifying Tank
Modern vacuum emulsifying tanks are engineered with features that ensure high performance, compliance with regulations, and ease of operation. When evaluating a pharmaceutical-grade emulsifying tank, buyers should consider the following key features:
Vacuum-Sealed Mixing Environment: The tank carries out emulsification in a fully enclosed vacuum chamber, preventing exposure to air. This avoids oxidation of sensitive ingredients and eliminates solvent evaporation or loss of volatile components. By mixing in a vacuum, the system also prevents environmental contamination, keeping both the product and the workspace clean and sterile.
High-Shear Homogenizer with Scraper Agitators: Inside the main tank, a high-speed rotor–stator homogenizer works in tandem with an agitator (often with wall scrapers). The high-shear mixer breaks down particles and droplets at thousands of RPM, while the slow-speed scraper agitator continuously folds product from the walls into the mixing zone. This dual-action mixing ensures even very viscous creams are uniformly emulsified with no “dead zones.” The emulsification process is so effective that it can produce extremely fine emulsions meeting nano-level particle size requirements for advanced ointments.
Precision Temperature Control (Heating/Cooling): Pharmaceutical emulsions often require controlled temperatures for optimal mixing or stability. Vacuum emulsifying tanks typically have a jacketed vessel for heating or cooling the batch. Electric heaters or steam in the jacket can heat the product to a set temperature, which is automatically regulated by an integrated temperature control system. Likewise, the jacket can circulate cooling water to rapidly bring the product to a desired temperature. This precise temperature control ensures that heat-sensitive actives are protected and that the final cream has the right consistency (for example, cooling under vacuum can help set a cream without air bubbles).

Driving Quality and Efficiency in Pharma Manufacturing
Investing in a vacuum emulsifying tank can be a game-changer for pharmaceutical production. It not only improves the quality of creams, lotions, and other emulsions but also boosts process efficiency. Grand Pack Emulsification Mixing report significantly shorter mixing times since vacuum conditions eliminate the lengthy de-aeration step that atmospheric mixers require. There’s no need to spend hours or days waiting for air bubbles to naturally rise out of a batch – the vacuum system has already done that during mixing. This means faster batch turnarounds and higher throughput for your production line. Additionally, by delivering a uniform and stable product, a vacuum emulsifying tank reduces batch reworks and rejects, which can save costs in the long run. From a compliance perspective, the sanitary design and robust controls help meet pharmaceutical GMP requirements with ease, simplifying validation and cleaning documentation.
In summary, the vacuum emulsifying tank has emerged as an invaluable tool for pharmaceutical cream production and beyond. Its combination of vacuum technology and high-shear mixing ensures that each batch of product is homogenuous, stable, and of the highest quality. For potential buyers – whether you produce prescription dermatological creams, over-the-counter ointments, or innovative drug delivery gels – adopting a pharmaceutical-grade vacuum emulsifying tank can significantly elevate your production capabilities. It marries advanced engineering with practical benefits, ultimately delivering smoother operations and superior products that can boost your brand’s reputation in a competitive market.
References:
Ross,Vacuum Mixing – Studies show that processing under vacuum reduces porosity and improves product quality. (Technical paper)
Yuxiang . (2024). The Science Behind Emulsions: How Vacuum Emulsifying Mixers Work. – Smaller droplets lead to more stable emulsions; high-speed vacuum emulsifier achieves nano-scale particle size.