How a High-Speed table Counting Machines Redefines Production Efficiency?

Tablet Press Maintenance: A Pill Press Lubrication Guide
How a Capsule Filling Machine Works: The Ultimate Guide for Pharma

A Deep Dive Into the Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
The humble capsule is a marvel of modern medicine. It’s a clean, simple, and effective way to deliver precise doses of medication, supplements, and vitamins. But have you ever stopped to wonder about the incredible journey that transforms a fine powder into the perfectly formed capsule you see in the bottle? The hero of this story is a piece of high-precision engineering: the CFK capsule filling machine series.
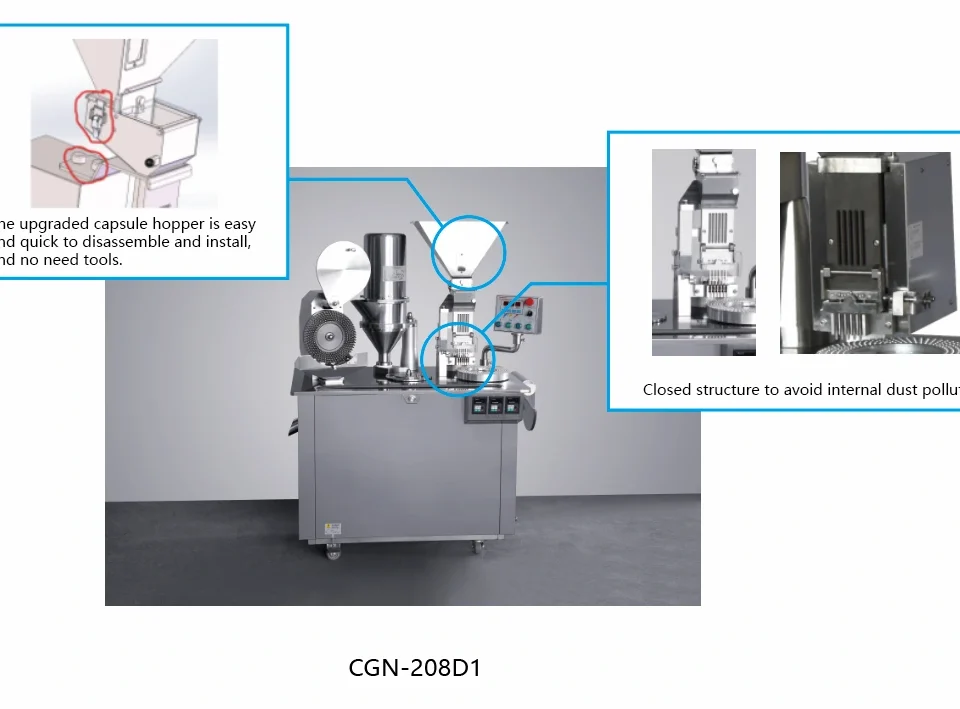
For any pharmaceutical manufacturer, investing in the right equipment is the cornerstone of success. It dictates production speed, dose accuracy, product quality, and ultimately, patient safety. This is where the magic of automation comes in. Today, we're taking a deep dive into the sophisticated inner workings of a fully automatic capsule filling machine, exploring the complex, ballet-like process that happens inside. We’ll be looking at the advanced technology, like that found in Grand's CFK-1250, to understand how these machines have become the backbone of modern pharmaceutical production.

The Challenge: Precision at Scale
Before automation, filling capsules was a tedious, inconsistent, and labor-intensive process. Manual and even semi-automatic capsule filling machine models, while useful for small-scale or R&D applications, struggle to meet the demands of large-scale manufacturing. They face challenges with maintaining fill-weight uniformity, preventing cross-contamination, and achieving high output rates.
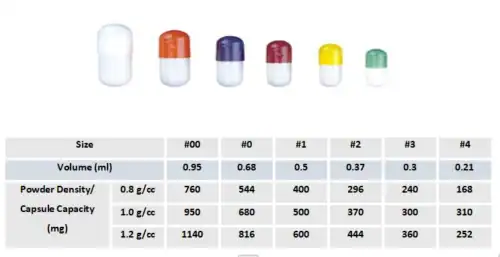
Empty capsule model comparison chart
The pharmaceutical industry demands near-perfect precision. A slight deviation in the amount of capsule-filling powder can have significant consequences for a drug's efficacy. Furthermore, with the growing popularity of different capsule materials, including traditional gelatin and plant-based vegetable capsules, modern machines must be versatile enough to handle them all with delicate precision. This is the problem that fully automatic, rotary-turret systems were designed to solve.
The Heart of the Machine: A 10-Station Symphony of Production
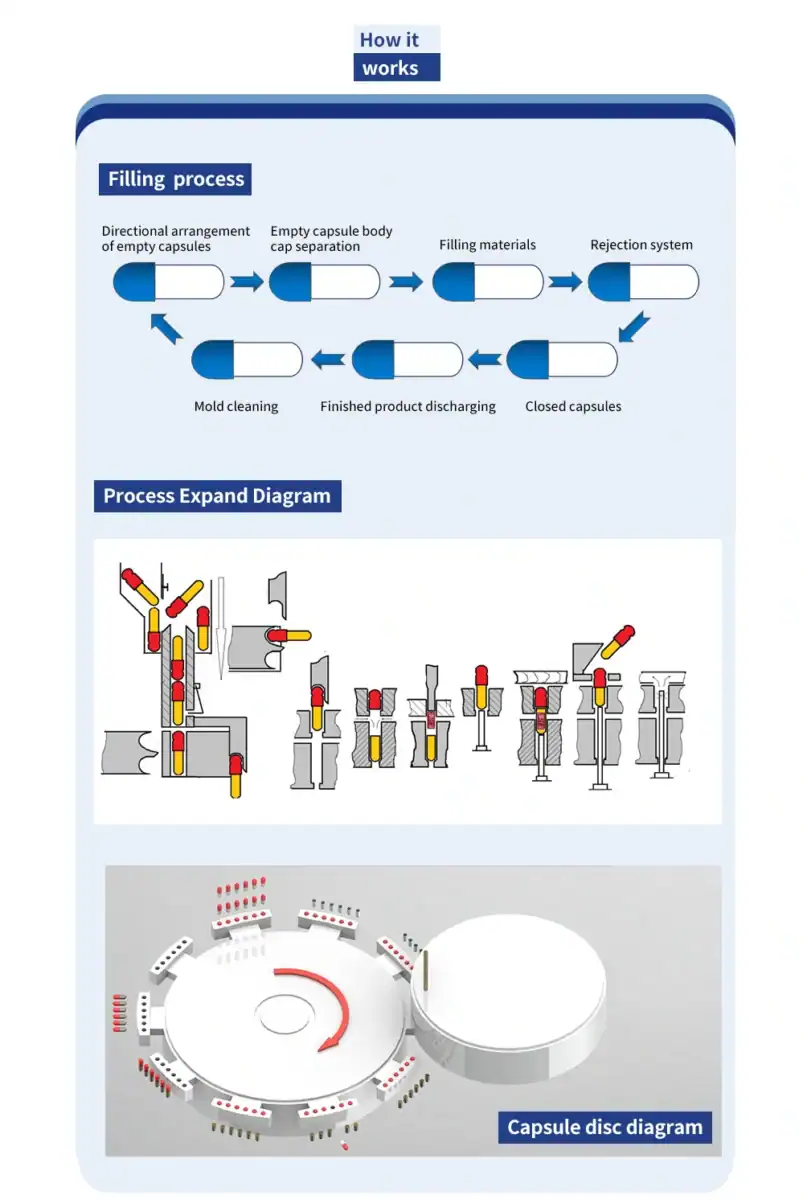
Imagine a circular stage where a series of highly specialized tasks are performed in perfect synchronization. This is the essence of an intermittent rotary turntable, the core component of a modern automatic capsule machine. The Grand CFK-1250, for example, utilizes a fully enclosed, ten-station turntable where each step of the encapsulation process is executed flawlessly.
Let’s walk through this intricate process, station by station.
Station 1: Capsule Orientation and Separation
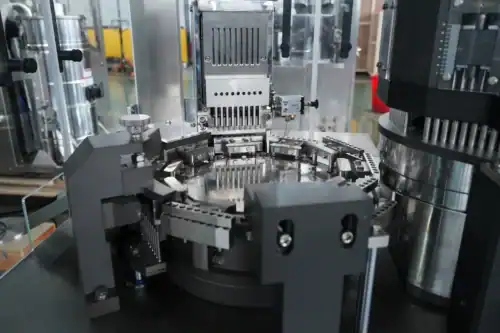
It all begins at the loading station. A hopper full of empty capsules feeds them into the system. A clever mechanism, often using a horizontal fork, ensures each capsule is oriented correctly, typically body-downwards. Once aligned, the capsules are inserted into segmented die plates on the turntable. A vacuum is then applied from below, which gently pulls the capsule body down while the cap is held in an upper segment. This "great separation" is a critical first step, opening the capsule body to receive its contents.
Stations 2, 3, 5, 7: Reserved for Versatility

A key feature of advanced filling machines is modularity. Several stations are often reserved or designed to be free, allowing for immense flexibility. These can be configured for optional pellet or tablet filling stations, allowing for complex combination therapies within a single capsule. This adaptability is crucial for contract manufacturers and companies with diverse product lines.
Station 4: The Dosing Station - Where Precision is Paramount

This is where the core filling action happens. The most common and reliable method is the "dosator" or "tamping pin" principle. Here’s how it works:
- Powder Bed: A hopper maintains a consistent bed of the formulation (powder or pellets).
- Dosator Entry: A set of hollow tubes, or dosators, plunges into the powder bed.
- Compaction: A series of tamping pins inside the dosators compress the powder in multiple stages. This compaction is crucial for creating a cohesive "slug" of powder with a uniform density.
- Transfer & Ejection: The turntable rotates, moving the filled dosators over the empty capsule bodies. The tamping pins then gently push the precisely metered powder slug out of the dosator and into the capsule body.

The accuracy here is astounding, with high-end machines like the CFK-1250 Capsule filling machine achieving a filling error as low as ±2-3.5%. This precision isn't accidental. It’s the result of features like three-dimensional adjustment mechanisms on the metering plate, which minimize powder leakage and ensure every dose is consistent. As research from academic reviews on capsule filling points out, powder flowability and compressibility are significant variables. Advanced machines are designed to control these factors through precise, repeatable mechanical actions.
Station 6: Faulty Capsule Rejection

Quality control is integrated directly into the process. This station is dedicated to identifying and removing any capsules that failed to separate correctly. If a cap and body are still joined, a pin will detect this and eject the entire faulty capsule, ensuring that only properly opened capsules proceed to the filling stage and that no unfilled capsules make it to the final batch.
Station 8: Capsule Closing
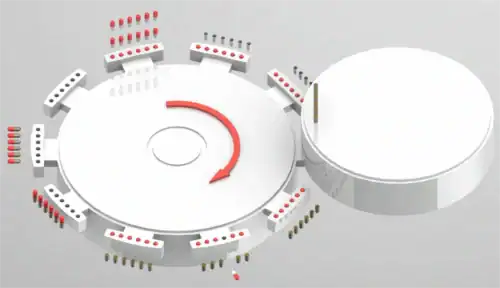
With the body filled, it’s time for reunification. The upper and lower turntable segments, holding the caps and filled bodies respectively, are brought back together. A set of locking pins applies gentle, uniform pressure to securely join the two halves, creating a sealed, tamper-evident capsule. A noteworthy innovation in modern machines is a cleaning device at this station, which vacuums away any fine dust that might have been raised during the locking process, ensuring a cleaner final product.
Station 9 & 10: Ejection and Cleaning
The journey is almost complete. The finished, qualified capsules are ejected from the turntable segments into an outlet chute, ready for the next stage of production.
Finally, the now-empty segments pass through a cleaning station. Here, jets of compressed air blow out any residual powder from the die holes. This step is especially critical when working with highly viscous or sticky powders that can build up over time, ensuring the mold is perfectly clean for the next cycle and improving the success rate of capsule insertion.
Engineering Excellence: Beyond the Basic Functions
A truly superior capsule filling machine is defined by more than just its process. It's about the underlying engineering that ensures reliability, longevity, and compliance.
- Stability is Key: The high-speed, intermittent motion of the turntable can generate significant vibration. Top-tier machines incorporate a high-precision, high-configuration transmission mechanism. This robust design minimizes vibration, leading to smoother operation, higher accuracy, reduced wear and tear, and a much longer service life.
- GMP Compliance and Cleanliness: Pharmaceutical manufacturing operates under strict Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Machines designed for this environment feature fully enclosed turntables to prevent contamination. Furthermore, modular powder filling mechanisms and easy-to-disassemble parts make cleaning and changeovers faster and more thorough.
- Intelligent Control: The brain behind the brawn is a sophisticated control system. The use of world-class electronic components from brands like Siemens and OMRON, combined with an advanced PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), ensures every movement is perfectly timed and controlled. A modern, dust-proof human-machine interface (HMI) provides operators with intuitive controls, real-time diagnostics, and complete oversight of the production process.
Building a Complete Production Line
The journey of a capsule doesn't end when it's filled. A highly efficient pharmaceutical operation requires a seamless production line. The filled capsule is just the beginning. This is why it's essential to partner with a provider that understands the entire workflow.
After leaving the capsule filling machine, the capsules(Capsule dosage formare) typically polished and sorted before heading to packaging. The next critical piece of equipment is often a Grandpack blister pack machine, which seals the capsules into individual, protected pockets. This machine must integrate smoothly with the filler's output to maintain a continuous flow. From there, the blister packs are sent to a cartoning machine for final packaging.
Grand specializes in providing these comprehensive, integrated solutions. From high-capacity automatic fillers to flexible semi-automatic capsule filling machine models for smaller batches, and through to downstream blister packers and cartoners, we can help you build a robust, efficient, and compliant capsule production line tailored to your specific needs.
Choosing the right capsule filling machine is an investment in the quality, safety, and efficiency of your entire manufacturing process. By understanding the intricate, high-precision dance happening inside these remarkable machines, you can make a more informed decision and equip your facility for a future of pharmaceutical excellence.
References
1.The Ultimate Guide to Capsule Polishing Machines
2.What Is a Capsule Filling Machine? Everything You Need To Know