Top 10 Softgel Machine Manufacturers In The World(2025)

Overview of China’s Tablet Press Market
Tablet Press Machine; Types, Working Principle, Production Steps All You Need To Know
Quick Overview
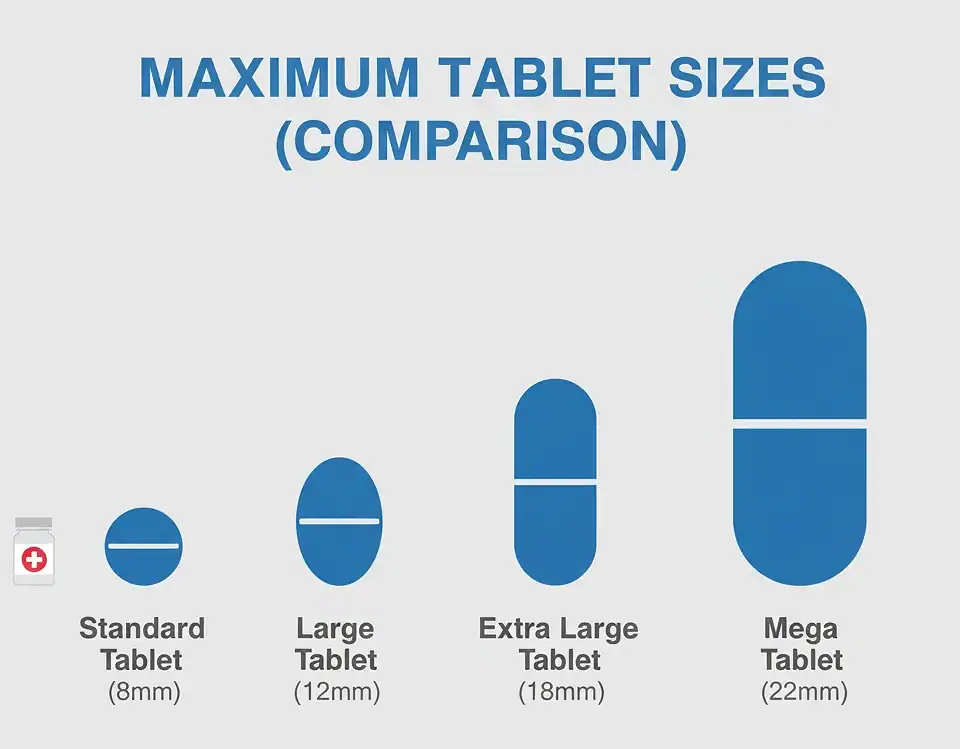
Tablet press machines are mainly used for research and development in tablet production within the pharmaceutical industry. These machines automatically compress granular materials into tablets of different shapes, such as round or custom designs, often featuring text, symbols, or graphics, with a diameter of up to 13mm. Some machines may generate burrs and dust during the process, so they need to be paired with a tablet screener for dust removal, typically done twice. They also must adhere to GMP standards to ensure quality and safety.
Tablet Press Machine Types:
Tablet press machine: A machine that compresses dry granules or powder into tablets using molds.
Single-punch tablet press:A press with a single mold that moves up and down to form tablets.
Rotary tablet press: A machine with multiple molds arranged on a rotating turntable, moving up and down along a set path to make tablets.
High-speed rotary tablet press:A rotary press where the molds rotate with the turntable at a speed of at least 60 meters per minute.
Principles of tablet compression:
Dose control:
Different tablets require different doses. Different punch molds are used to make large adjustments. Once the mold size is chosen, smaller adjustments can be made by changing how deep the lower punch goes into the die. This alters the volume inside the die, controlling how much drug is filled into the mold. Tablet presses have a mechanism that allows the lower punch to be adjusted to meet the required dosage.

Dose Control
Controlling tablet thickness and compression:
While the prescription fixes the drug dosage, the pressure used during compression can be adjusted. This pressure affects how thick, firm, and smooth the tablet turns out, which matters for things like storage, transport, and how quickly the tablet breaks down. Pressure is usually controlled by adjusting how far the upper punch moves down.
Some machines allow both the upper and lower punches to move at the same time, working together to compress the tablet. However, most of the time, the upper punch's movement controls the pressure.
How does a tablet press machine work?
1. The lower punch moves into the die from below, sealing the bottom of the die cavity.
The lower punch moves up into the die and seals the bottom of the cavity. This holds the powder or granules in place so they can be compressed into a tablet. It’s an important step to make sure the tablet forms properly. The tablet won’t come out right if the seal isn't tight.

Step 1
2. A feeder fills the die cavity with the drug powder.
The feeder drops the drug powder into the die cavity, making sure it’s filled. This step is crucial for getting the right amount of powder for each tablet. It ensures the dosage is accurate and the tablets are consistent. Once the cavity is filled, the powder is ready to be compressed.
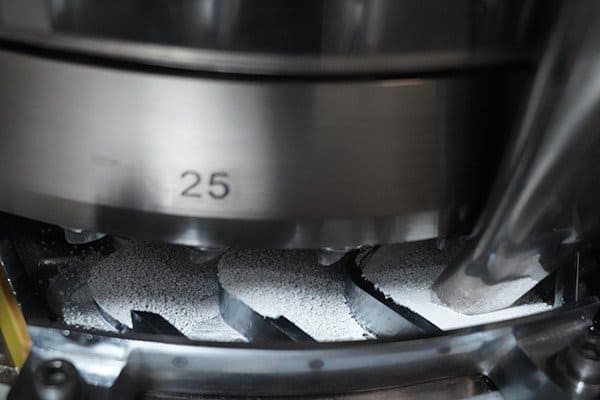

Step 2
3. The upper punch then moves down into the die, compressing the powder into a tablet.
The upper punch moves down into the die, pressing the powder into a solid tablet. This pressure is what gives the tablet its shape and strength. The right amount of force is crucial to make sure the tablet holds together properly. If it’s not compressed enough, the tablet could crumble later. Once it’s formed, the tablet is ready to be pushed out and used.
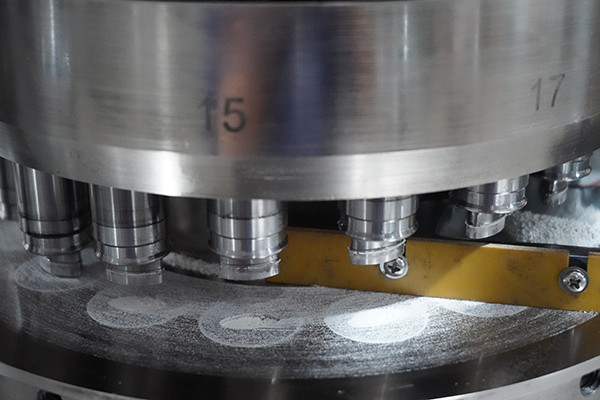

Step 3
4. The upper punch lifts out, and the lower punch rises to eject the tablet from the die.
The upper punch lifts up, and the lower punch pushes the tablet out of the die. This gently ejects the finished tablet from the machine without damaging it. Once it’s out, the tablet is ready for whatever comes next, like coating or packaging. The machine then gets set up for the next tablet.
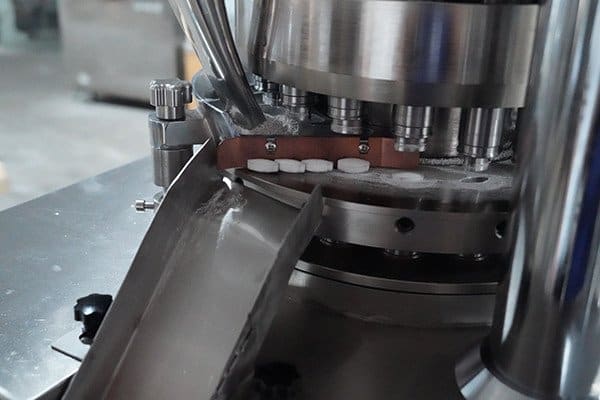

Step 4
5. The lower punch then returns to its starting position, ready for the next round of filling.
The lower punch goes back to its starting position after pushing out the tablet. It’s now ready for the next batch of powder to be added. This quick reset keeps the process moving smoothly. Once it’s in place, the die can be filled again, and the cycle starts over to keep making tablets.
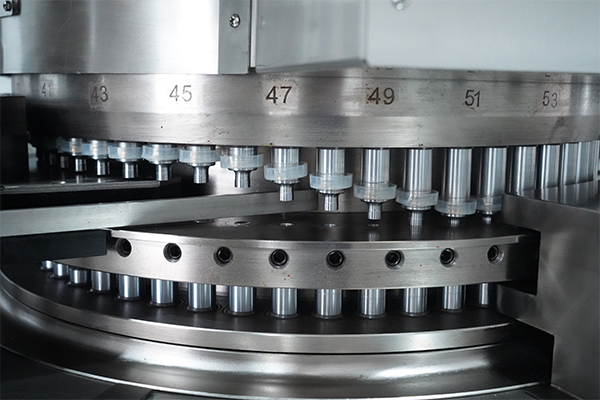

Step 5
Structure of the tablet press machine:
A tablet press is a machine used to compress powdered or granular materials into tablets. The material is placed into a die, and punches are used to compress it into shape. Early tablet presses had a single punch that moved up and down to form tablets. These were called single-punch presses and later evolved into electric basket-type presses.
The early machines still relied on a single-sided compression method where only the upper punch applied pressure while the lower punch stayed still. This often led to uneven density in the tablets, causing problems like cracking. To fix this, rotary multi-punch double-sided presses were developed.
Rotary presses use both the upper and lower punches to apply pressure evenly. This allows air to escape from the material, creating tablets with more consistent density and reducing the chances of cracking. Rotary presses are also more efficient, producing less noise, vibration, and energy while ensuring more accurate tablet weights.
In rotary tablet presses, multiple sets of punches are arranged on a rotating turntable. The punches move up and down in a circular motion, compressing the material into tablets using rollers. When the punch rods rotate at speeds of 60 meters per minute or more, the machine is classified as a high-speed rotary press. These machines come with features like forced feeding, automatic pressure adjustment, and tablet weight control.
A PLC system controls high-speed rotary presses. They automatically reject defective tablets and stop the machine if there is an issue. The system can also identify and remove tablets with defects like chipping or cracking while ensuring that tablet weight differences remain within a set range.
Most tablets were originally flat and round. Over time, they evolved into shapes with shallow or deep curves on both sides, making them easier to coat. As shaped tablet presses were developed, new forms emerged, such as ovals, triangles, squares, and rings.
Pharmaceutical advancements led to the creation of special tablets like double-layer, triple-layer, and core-filled tablets, which require specialized machines. Growing demand has expanded the application of tablet presses beyond pharmaceuticals.
Tablet presses are now widely used for supplements, veterinary medicines, and chemical products. They can even produce household items like mothballs, detergent blocks, and food tablets. The versatility of these machines continues to increase as new needs emerge.
The Maintenance and Care of Rotary Tablet Presses
Proper maintenance of a rotary tablet press is not merely a recommendation; it is essential for ensuring consistent tablet quality, maximizing the machine's lifespan, and adhering to strict Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Based on its operational principles—from dosing and compression to ejection—a proactive maintenance schedule helps prevent common issues such as tablet cracking, weight variance, and cross-contamination. This guide outlines key maintenance procedures.
1. Post-Production / Daily Maintenance
This routine is crucial for cleanliness and immediate operational safety.
Thorough Cleaning: After every production batch, the machine must be meticulously cleaned. This involves removing all residual powder from the feeding mechanism, the turret surface, the die bores, and the punch guides. Use industry-approved vacuums and cleaning agents that won't damage the machine's surfaces. This step is critical to prevent cross-contamination between different batches and to comply with GMP standards.
Tooling Inspection: Remove, clean, and inspect all punches and dies. Look for any signs of wear, chipping, or sticking residue. Damaged tooling is a primary cause of defective tablets (e.g., cracking, capping) and can also damage the turret itself.
Dust Extraction System Check: Ensure the dust extraction nozzles and system are clear and functioning correctly. The article notes that tableting can produce dust, and an efficient extraction system is vital for operator safety and machine cleanliness.
2. Weekly Maintenance
Weekly checks focus on lubrication and calibration to ensure smooth, precise operation.
Lubrication: Proper lubrication is key for a machine with many high-speed moving parts. Lubricate all specified points according to the manufacturer's manual. This includes the punch heads, punch barrels, and the cam tracks that guide their vertical movement. Insufficient lubrication causes friction, wear, and excessive noise.
Inspection of Belts and Moving Parts: Check the tension and condition of the turret drive belt. Inspect the feeder mechanism for any loose parts or signs of wear.
Calibration Check: Verify the accuracy of the dosing and pressure control systems. Perform test runs to ensure that the tablet weight, thickness, and hardness are within the specified range. This validates that the lower punch’s fill depth and the upper punch’s compression distance are being controlled accurately.
3. Monthly and Periodic Maintenance
These more in-depth checks address long-term wear and tear.
Deep Tooling Care: Fully disassemble and deep clean the punch and die sets. Polish the die bores and punch tips to ensure a smooth surface, which aids in clean tablet ejection and prevents sticking.
Mechanical Inspection: Examine the compression rollers for any signs of surface damage or bearing wear. These rollers withstand immense pressure and are critical for uniform tablet density. Inspect the cam tracks for wear, as this can affect the smoothness of the punch movement and lead to inconsistent tablet quality.
PLC and Electrical Systems Check: For high-speed presses, ensure the PLC system and its associated sensors are functioning correctly. This includes the automatic rejection gate for faulty tablets and the pressure sensors that regulate compression force. Confirm that all safety stops and emergency switches are operational.
Record Keeping: Meticulously document all maintenance activities, including cleaning, parts replacement, and calibration results. This documentation is a fundamental requirement of GMP and is invaluable for troubleshooting future issues.
By following a structured maintenance plan, you ensure the rotary tablet press operates at peak efficiency, producing uniform, high-quality tablets while minimizing downtime and extending the life of this critical manufacturing asset.