The Role of the Modern Tablet Press in Creating the Perfect Tablet

How an Automatic Liquid Filling Machine (Reagent filling and sealing) Works?
The Heart of Modern Medicine: Capsule and Tablet Manufacturing
Introduction
From daily vitamins to life-saving medications, oral solid dosage forms—namely, capsules and tablets—are the bedrock of the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. While they may seem simple, their creation is a sophisticated process where science, precision engineering, and rigorous quality control intersect. The journey from a raw powder to a finished, effective product hinges on advanced machinery that ensures every single dose is perfect.

This guide will explore the intricate world of capsule and tablet manufacturing. We'll break down the key differences between hard and soft gelatin capsules, demystify the granulation process that prepares compression materials, and uncover the mechanical ballet of the tablet press machine. Throughout this exploration, we'll see how top-tier equipment, like that engineered by Grandpackmachine, is essential for achieving the highest standards of quality and efficiency that define a leader in the pharmaceutical field.
Capsules Uncovered: The Tale of Two Shells
Capsules are a popular choice for delivering active ingredients, prized for their ability to mask unpleasant tastes and for their ease of swallowing. They come in two primary forms: hard gelatin and soft gelatin (softgels).

Hard Gelatin Capsules: The Versatile Standard
Often called "two-piece" capsules, hard gelatin capsules consist of a cap and a body that fit together. They are typically filled with dry, solid materials like powders, granules, or pellets.
The manufacturing process is a marvel of precision:
- Gelatin Preparation: A solution of gelatin, water, and plasticizers is prepared and heated to a uniform consistency.
- Molding: Stainless steel pins, shaped like the capsule cap and body, are dipped into this solution. They are then carefully rotated and dried to form a solid, even shell.
- Filling and Sealing: Once dried, the two halves are separated. The body is filled with the active ingredient, and the cap is precisely fitted over it, often with a locking mechanism to create a tamper-evident seal.
Hard capsules are prized for their versatility and rapid dissolution in the stomach, allowing for quick absorption. However, their primary limitation is their sensitivity to moisture and unsuitability for certain oily liquids.
Soft Gelatin Capsules (Softgels): The Liquid Specialists
Softgels are single-piece, hermetically sealed capsules designed to hold liquids, oils, or active ingredients suspended in a liquid base. Their gelatin shell is thicker and more flexible than that of hard capsules.
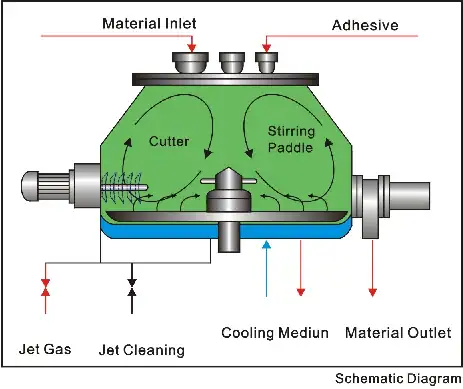
The production of softgels is more complex and requires specialized equipment, like the Grand softgel capsule making machine:
- Gelatin Mixture: A similar gelatin mixture is prepared, but with a higher concentration of plasticizers to create a more pliable shell.
- Rotary Die Encapsulation: This is the core of the process. Two continuous ribbons of warm gelatin are fed between a pair of rotating dies. Simultaneously, the liquid fill material is precisely injected between the ribbons just as the dies meet. The heat and pressure from the dies form, fill, and seal the softgel in one seamless motion.
- Drying: The freshly formed softgels are then carefully dried to remove excess moisture, which hardens the shell and ensures stability.
Softgels are ideal for enhancing the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs and protecting sensitive ingredients from oxidation. Their smooth texture also makes them exceptionally easy to swallow. The journal Science has published research highlighting how lipid-based drug delivery systems, often encapsulated in softgels, can dramatically improve the absorption of certain compounds. This underscores the critical role that advanced encapsulation technology plays in drug efficacy.
Granulation: The Crucial Step Before the Press
Before most powders can be effectively compressed into tablets or filled into capsules, they must undergo granulation. This process agglomerates fine powder particles into larger, more uniform granules. Why is this so important? It dramatically improves two key properties: flowability and compressibility. Without good flow, it's impossible to ensure each tablet or capsule gets the same amount of powder, leading to dangerous dosage variations.
There are two primary methods of granulation:
Wet Granulation: The Gold Standard
This is the most common method, renowned for producing highly uniform and compressible granules. The process involves:
- Mixing the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
- Adding a liquid binder to the powder mix to form a wet mass.
- Passing this mass through a granulator (like the Grand Rapid Mixing Pharma Granulator) to form granules.
- Drying the granules to the optimal moisture content.
- Sieving the granules to ensure a consistent size.
Wet granulation is excellent for low-dose drugs where content uniformity is paramount.
Dry Granulation: The Moisture-Free Alternative
This method is used for ingredients that are sensitive to moisture or heat. Instead of a liquid binder, it uses mechanical force.
- The powder blend is first compacted into large "slugs" or sheets using a roller compactor (like the Grand Dry Granulation Machine).
- These slugs are then milled and sieved into the desired granule size.
Dry granulation is simpler and more energy-efficient, but it can generate more dust and is best suited for naturally compressible materials.
The choice between wet and dry granulation is a critical decision in pharmaceutical development. The ability to execute both processes flawlessly, supported by high-quality machinery, is a hallmark of a proficient manufacturer.
The Tablet Press: Forging Medicine with Force and Precision
At the heart of tablet production is the tablet press machine. This powerful device compresses granulated material into a solid, uniform tablet with incredible speed and accuracy. While single-punch presses exist for R&D, modern production relies on the rotary tablet press.
A rotary press features a rotating turret that holds multiple sets of punches and dies. Its operation is a continuous, cyclical process:
- Filling: As the turret rotates, the lower punches drop within the dies, creating a cavity that is then filled with a precise volume of granules from a feeder.
- Compression: The turret carries the filled dies between large compression rollers. The upper punches descend, and the rollers apply immense, controlled pressure from both above and below, compacting the granules into a solid tablet. This dual-sided compression is crucial for creating tablets with uniform density and preventing defects like cracking. As research in journals like Cell has shown on a molecular level, the uniform application of force is critical to forming stable crystalline structures in solids. This principle is mirrored in the macroscopic world of tablet pressing, where the mechanical precision of a Grandpackmachine press ensures each tablet has the structural integrity to withstand handling and dissolve correctly.
- Ejection: After compression, the upper punches retract, and the lower punches rise to eject the finished tablet from the die, ready for the next stage of production.
High-speed rotary presses can produce hundreds of thousands of tablets per hour. They are equipped with advanced PLC systems that automatically monitor and adjust for tablet weight, thickness, and hardness, rejecting any tablets that fall outside the strict specifications. This level of automation and control is what separates good manufacturing from great manufacturing.
Conclusion: The Grandpackmachine Standard of Excellence
Creating the perfect capsule or tablet is a symphony of complex processes. From the choice between a hard or soft gelatin shell to the selection of a wet or dry granulation method, and finally to the precise moment of compression in a tablet press, every step demands expertise and flawless execution.
The common thread weaving through all these critical stages is the absolute necessity for superior machinery. The construction quality, precision engineering, and advanced control systems found in Grandpackmachine equipment are not just features—they are the foundation of reliable, repeatable, and GMP-compliant pharmaceutical production. Whether it's a softgel encapsulator, a granulator, or a high-speed tablet press, this commitment to excellence is what makes Grandpackmachine a true leader in the professional pharmaceutical field, empowering manufacturers to deliver the safe and effective medicines the world relies on.